Database backup and recovery Overview:
What is database backup?
- Keeping a secondary copy of the information from several locations.
- Useful in case primary database crash or failure.
- A way to protect and restore the database.
Why Backup?
- In order to restore and recover the corrupted or damaged file for the continuous function of an application.
Who does it?
- Generally, RDBMS or similar database management software does it.
How to recover?
- Database Administrator use backup files to restore the database to its operational state.
Difference between Backup and Archive.
Backup:
- A secondary copy of the information.
- Use for the recovery operation. Improve database availability by enabling the application to restore to a specific point in time.
- Typically short term (Weeks or month).
Archive:
- A primary copy of the information.
- Available for information retrieval.
- Adds operational effectiveness by moving content out of the operating environment.
- Typically long term (months, years, Decade)
Restoring and Recovery:
- Process of copying backed up data from secondary storage to the original location.
- Perform to return data that has been lost or damaged.
- Operation is generally done after a crash, failure, or disaster.
- The database gets recovered after restoring backed up files.
Circumstances that lead to restoration.
- Human error:- Data get accidentally deleted or damaged.
- Power outage:- Removing unsaved files.
- Malicious-attack:- Data theft, infected with the virus, hacking, etc.
- Man-made or natural disaster.
- Equipment, theft, malfunction, or failure.
- Firmware corruption.
Defining backup and recover strategy:
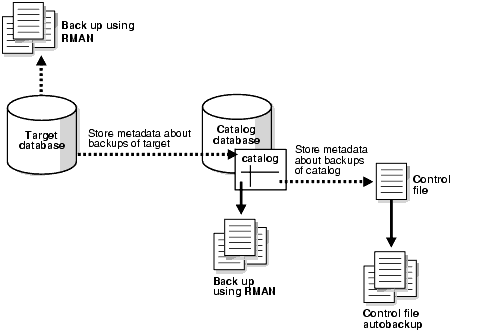
There are two ways to perform oracle database
- Oracle recovery manager (RMAN)
- RMAN keeps backup.
- RMAN is installed during the oracle server installation.
2. User managed backup and recovery:
-
- Using OS command
- Using SQL*PLUS commands.
| RMAN |
Backup and recovery consideration:
- Business operational and technical consideration/
- Components of disaster recovery plans.
- Importance of testing backup and recovery strategy.
Responsibilities of DBA for maintaining recover-ability:
- To keep the number of backup failures to a minimum, maximum data availability.
- Spent less time in recovering, maximize recovery, recovery performance.
- Minimize or avoid data loss, maximize data recover-ability.
Business Consideration:
- Understand the business use of the system.
- convince the system owners and management about the cost of maintaining system ability.
- Cost assessment for maintaining availability.
Components of the recovery plan:
- What disaster recovery scenarios can occur on the system?
- What disaster recovery scenarios involve recovery from data loss?
- How volatile is data stored on the system ?
- How quickly does the system need to be made available?
- How does the cost providing a recovery strategy for any scenarios evaluated against the cost of losing time to re-enter the data? ?
- The answers to these questions define the backup and recovery plan.
Importance of testing and backup recovery strategy:
- What is the testing of backup recovery?
- It is the process of accessing the effectiveness of software to replicate data for security and checking the ability to reliably retrieve data.
- Backup and recovery testing is an essential part of the disaster recovery plan.